Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O (
( : rare earths)
: rare earths)Yoshii, Kenji; Funae, Takeshi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Ejiri, Hiroki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Matsumura, Daiju
Physica Status Solidi (C), 12(6), p.841 - 844, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.68(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report the effects of elemental substitutions in multiferroic  Fe
Fe O
O (
( : Y, Ho-Lu, In). The substitution by nonmagnetic Ga
: Y, Ho-Lu, In). The substitution by nonmagnetic Ga at the Fe site, which has not been reported so far, shows a drastic decrease in the ferrimagnetic transition temperature (
at the Fe site, which has not been reported so far, shows a drastic decrease in the ferrimagnetic transition temperature ( ). This is plausibly owing to the suppression of magnetic interactions between Fe ions, based on our previous results of other substituted systems such as
). This is plausibly owing to the suppression of magnetic interactions between Fe ions, based on our previous results of other substituted systems such as  FeCoO
FeCoO . Dielectric constants near room temperature were comparable to those of
. Dielectric constants near room temperature were comparable to those of  Fe
Fe O
O . The suppression of dielectric loss in this system is suitable to application. The
. The suppression of dielectric loss in this system is suitable to application. The  -site substitution was also attempted by the large R
-site substitution was also attempted by the large R ions such as Dy
ions such as Dy . The solubility limit was up to about 10% of
. The solubility limit was up to about 10% of  ions, as confirmed by XRD and EXAFS measurements.
ions, as confirmed by XRD and EXAFS measurements.  was raised by 5-10 K for Dy
was raised by 5-10 K for Dy substitution.
substitution.
 studied by X-ray spectroscopy
studied by X-ray spectroscopyMizumaki, Masaichiro*; Fujii, Hitoshi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Hayashi, Naoaki*; Saito, Takashi*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*; Uozumi, Takayuki*; Takano, Mikio*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 12(6), p.818 - 821, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:94.45(Physics, Condensed Matter)We investigated the electronic structure of BaFeO by using HAXPES and XAS measurements and first principle studies. The experimental and theoretical results indicated that BaFeO
by using HAXPES and XAS measurements and first principle studies. The experimental and theoretical results indicated that BaFeO is a negative charge transfer compound. We concluded that the on-site Coulomb energy and the strong hybridization between Fe-3d and O-2p orbitals play a very important role of emergence of negative charge transfer. And we found the new structure in the Fe-2p XPS spectrum and concluded this structure is originated from non-local screening.
is a negative charge transfer compound. We concluded that the on-site Coulomb energy and the strong hybridization between Fe-3d and O-2p orbitals play a very important role of emergence of negative charge transfer. And we found the new structure in the Fe-2p XPS spectrum and concluded this structure is originated from non-local screening.
 -FeSi
-FeSi film on Si(100)
film on Si(100)Yamaguchi, Kenji; Hamamoto, Satoshi*; Hojo, Kiichi
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(12), p.1699 - 1703, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Effect of substrate treatment conditions, deposition temperature and deposition rate on the crystallinity of  -FeSi
-FeSi films formed on Si substrate was investigated. The substrates were treated with Ne
films formed on Si substrate was investigated. The substrates were treated with Ne ion beams at room temperature and then annealed at 1073 K prior to film fabrication by means of ion beam sputter deposition (IBSD) method. Combinations of experimental parameters which promote the epitaxial relationship of
ion beams at room temperature and then annealed at 1073 K prior to film fabrication by means of ion beam sputter deposition (IBSD) method. Combinations of experimental parameters which promote the epitaxial relationship of  -FeSi
-FeSi (100) // Si (100) were defined. Complicated dependence of these experimental parameters on the film structure indicated that careful optimization of substrate treatment conditions and deposition parameters would enable to obtain
(100) // Si (100) were defined. Complicated dependence of these experimental parameters on the film structure indicated that careful optimization of substrate treatment conditions and deposition parameters would enable to obtain  -FeSi
-FeSi films with excellent crystalline properties.
films with excellent crystalline properties.
 Mn
Mn Si/Ge(111) heteroepitaxial interfaces
Si/Ge(111) heteroepitaxial interfacesNoguchi, Masaya*; Hirata, Tomoaki*; Kawakubo, Yuki*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji; Maeda, Yoshihito
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(12), p.1732 - 1734, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) (Mn
(Mn Fe
Fe )Si(111) epitaxially grown on Ge(111)
)Si(111) epitaxially grown on Ge(111)Kawakubo, Yuki*; Noguchi, Masaya*; Hirata, Tomoaki*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji; Yamada, Shinya*; Hamaya, Kohei*; Miyao, Masanobu*; Maeda, Yoshihito
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(12), p.1828 - 1831, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Si/FeSi
Si/FeSi artificial lattices
artificial latticesSakai, Kenichiro*; Noda, Yuta*; Takeda, Kaoru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Yoshitake, Tsuyoshi*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(12), p.1862 - 1865, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.01(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Sasaki, Takuo; Norman, A. G.*; Romero, M. J.*; Al-Jassim, M. M.*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Kojima, Nobuaki*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(11), p.1640 - 1643, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:83.55(Physics, Applied)Kubo, Katsunori
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(3), p.544 - 548, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:89.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) and analysis of oxygen diffusion in PuO
and analysis of oxygen diffusion in PuO and (Pu,U)O
and (Pu,U)O
Kato, Masato; Uchida, Teppei; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(2), p.189 - 192, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:89.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) pellet
pelletUchida, Teppei; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Kato, Masato
Physica Status Solidi (C), 10(2), p.193 - 196, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:86.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals
nanocrystalsMaeda, Yoshihito; Nishimura, Kentaro*; Nakajima, Takahito*; Matsukura, Bui*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji
Physica Status Solidi (C), 9(10-11), p.1884 - 1887, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:88.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report enhancement of intrinsic photoluminescence (PL) from  -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals by doping carbon. In the appropriate dose of C
nanocrystals by doping carbon. In the appropriate dose of C
 ion implantation into the average nanocrystal size of 14 nm, the PL intensity was enhanced by 260% and increase of the exciton binding energy of 1.8 meV in comparison with that of the non-doped nanocrystal. Furthermore, we found that there was a clear correlation between the PL enhancement and increase of the exciton binding energy. This important result suggests that carbon atoms doped in the silicide lattice may play as an isoelectronic trap and probably form bound excitons with stable states as predicted theoretically. We found a new mechanism of the PL enhancement for
ion implantation into the average nanocrystal size of 14 nm, the PL intensity was enhanced by 260% and increase of the exciton binding energy of 1.8 meV in comparison with that of the non-doped nanocrystal. Furthermore, we found that there was a clear correlation between the PL enhancement and increase of the exciton binding energy. This important result suggests that carbon atoms doped in the silicide lattice may play as an isoelectronic trap and probably form bound excitons with stable states as predicted theoretically. We found a new mechanism of the PL enhancement for  -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals.
nanocrystals.
 -FeSi
-FeSi nanocrystals embedded in Si
nanocrystals embedded in SiMaeda, Yoshihito; Nishimura, Kentaro*; Nakajima, Takahito*; Matsukura, Bui*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Sakai, Seiji
Physica Status Solidi (C), 9(10-11), p.1888 - 1891, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:83.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have systematically investigated photoluminescence (PL) properties of  -phase nanocrystals which are formed by a phase transition from metastable
-phase nanocrystals which are formed by a phase transition from metastable  -FeSi
-FeSi with a Fluorite structure to
with a Fluorite structure to  -FeSi
-FeSi , and succeeded in enhancement of the PL intensity in the optimum conditions of double annealing process. For the PL enhancement, the time of postannealing at 800
, and succeeded in enhancement of the PL intensity in the optimum conditions of double annealing process. For the PL enhancement, the time of postannealing at 800 C is dominated by the time of the preannealing at 400 or 500
C is dominated by the time of the preannealing at 400 or 500 C which is related to amount of the
C which is related to amount of the  -phase. After discussing some possible factors, we speculate that the PL enhancement observed in this study may be attributed mainly to improvement of the interface condition between the nanocrystal and Si, because the crystallographic epitaxial relationship among the phases, Si(111)//
-phase. After discussing some possible factors, we speculate that the PL enhancement observed in this study may be attributed mainly to improvement of the interface condition between the nanocrystal and Si, because the crystallographic epitaxial relationship among the phases, Si(111)// (111)//
(111)// (202)/(220) can be maintained during precipitation of the nanocrystal on Si(111).
(202)/(220) can be maintained during precipitation of the nanocrystal on Si(111).
Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Nath, K. G.*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 9(6), p.1450 - 1453, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.67(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Konishi, Tomoya*; Nishiwaki, Nagatoshi*; Tojo, Takashi*; Ishikawa, Takuma*; Teraoka, Teruki*; Ueta, Yukiko*; Kihara, Yoshifumi*; Moritoki, Hideji*; Tono, Tatsuo*; Musashi, Mio*; et al.
Physica Status Solidi (C), 8(2), p.405 - 407, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:74.8(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Okada, Hiroshi*; Takemoto, Kazumasa*; Oikawa, Fumitake*; Furukawa, Yuzo*; Wakahara, Akihiro*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi
Physica Status Solidi (C), 6(Suppl.2), p.S631 - S634, 2009/05
Light emitting field effect transistor (FET) based-on AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) structure with spatially selective doping of rare-earth ions (REIs) as a luminescence center in the channel is proposed and investigated. Fabricated device showed excellent I-V characteristics as a transistor with gate control. By applying a drain bias of 20 V, red emission suggesting a luminescence from Eu ion was clearly observed. Applying a negative bias to the Schottky gate decreased the luminescence intensity.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Fukaya, Yuki*; Hayashi, Kazuhiko; Hashimoto, Mie; Ichimiya, Ayahiko
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(10), p.3924 - 3927, 2007/09
Well-focused and highly parallel positron beam is totally reflected at the first surface layer when grazing incidence at a small enough angles. Therefore, the reflection high-energy positron diffraction (RHEPD) is suited to determine the surface structures without any disturbance from the bulk. Using the electro-magnetic lenses we developed a positron beam which has more coherence than before. We found that the RHEPD pattern from the Si-7 7 surface is considerably different from that of electron diffraction. The difference is reasonably explained as a strong thermal diffuse scattering of positrons. As a further application, we studied the phase transition of Si-Ag ultra-thin film. We found that the surface-sensitive diffraction spots exhibit significant temperature dependences. Based on the dynamical diffraction theory, the temperature dependences are reproduced considering the order-disorder phase transition. This will terminate the long debates in the surface science community. Furthermore, we recently found that the positron-surface interaction is different from the electron-surface interaction, especially in the elastic processes. We present the above recent advances of surface studies using RHEPD.
7 surface is considerably different from that of electron diffraction. The difference is reasonably explained as a strong thermal diffuse scattering of positrons. As a further application, we studied the phase transition of Si-Ag ultra-thin film. We found that the surface-sensitive diffraction spots exhibit significant temperature dependences. Based on the dynamical diffraction theory, the temperature dependences are reproduced considering the order-disorder phase transition. This will terminate the long debates in the surface science community. Furthermore, we recently found that the positron-surface interaction is different from the electron-surface interaction, especially in the elastic processes. We present the above recent advances of surface studies using RHEPD.
Yu, R.; Maekawa, Masaki; Miwa, Yukio; Hirade, Tetsuya; Nishimura, Akihiko; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(10), p.3577 - 3580, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.32(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Employing a positron beam with lateral resolution of about 30 micometer, we performed one and two dimensional scan of crack tips in mechanically fatigued as well as stress corrosion cracked (SCC) stainless steels. Results suggest the existence of quite different crack failure mechanisms in the two types of specimen. In agreement with normal crack propagation principal, creation of dislocations and vacancies close to a crack in the mechanically fatigued sample lead to an expected narrowing of the positron annihilation 511 keV Doppler broadening  -ray peak (S(crack)/S(bulk)=1.01). Contrarily, widening of the Doppler broadening peak was observed for the SCC specimen (S(crack)/S(bulk)=0.97). Such phenomenon was ascribed to the micro-compositional and micro-structural differences between the studied samples.
-ray peak (S(crack)/S(bulk)=1.01). Contrarily, widening of the Doppler broadening peak was observed for the SCC specimen (S(crack)/S(bulk)=0.97). Such phenomenon was ascribed to the micro-compositional and micro-structural differences between the studied samples.
Maekawa, Masaki; Yu, R.; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(10), p.4016 - 4019, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.32(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
Hirade, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Naoki*; Saito, Fuminori*; Hyodo, Toshio*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(10), p.3714 - 3717, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:82.43(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Positronium (Ps) can be formed by a reaction of trapped electrons and free positrons at low temperatures in molecular solids. While Ps formation by Ore and spur process must be fast, Ps formation by trapped electrons and free positrons is possible even at later positron age. The evidence of this delayed Ps formation was obtained by age-momentum correlation measurement of electron-positron pair annihilation  -rays. In this work the
-rays. In this work the 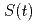 parameter curves measured with trapped electrons and no trapped electrons in polyethylene are interpreted by introducing possible positron reactions. Positrons that escape from Ps formation by the Ore and the spur processes have chance to form Ps with trapped electrons. This Ps formation competes with the positron localization resulting from the trapping between molecules or the weakly binding on molecules, ions, or radicals. Assuming the possibility of both the delayed Ps formation and delayed positron trapping and that S-parameters for ortho-Ps and free positrons are the same, we obtain a good fit to the observed time dependent S-parameter curves
parameter curves measured with trapped electrons and no trapped electrons in polyethylene are interpreted by introducing possible positron reactions. Positrons that escape from Ps formation by the Ore and the spur processes have chance to form Ps with trapped electrons. This Ps formation competes with the positron localization resulting from the trapping between molecules or the weakly binding on molecules, ions, or radicals. Assuming the possibility of both the delayed Ps formation and delayed positron trapping and that S-parameters for ortho-Ps and free positrons are the same, we obtain a good fit to the observed time dependent S-parameter curves 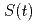 .
.
Chen, Z. Q.*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Naramoto, Hiroshi
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(10), p.3646 - 3649, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:56.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We implanted B , O
, O , Al
, Al , and P
, and P ions into ZnO (Dose: 4E+15/cm
ions into ZnO (Dose: 4E+15/cm ). The thermal recovery of implantation-induced defects were studied using a slow positron beam. S parameters show much increase after ion implantation, indication introduction of vacancy defects. The thermal recovery of these vacancies induced by different ions shows much difference. For O
). The thermal recovery of implantation-induced defects were studied using a slow positron beam. S parameters show much increase after ion implantation, indication introduction of vacancy defects. The thermal recovery of these vacancies induced by different ions shows much difference. For O implantation, vacancy clusters disappear rapidly after annealing up to about 700
implantation, vacancy clusters disappear rapidly after annealing up to about 700 C. For the lighter ion B
C. For the lighter ion B implantation, however, vacancy clusters grow to a larger size at 500
implantation, however, vacancy clusters grow to a larger size at 500 C. The vacancies begin to recover and disappear after further annealing up to 900
C. The vacancies begin to recover and disappear after further annealing up to 900 C. For the Al
C. For the Al implantation, the vacancies grow into even a much larger size after annealing at 600
implantation, the vacancies grow into even a much larger size after annealing at 600 C, and they are annealed out at 900
C, and they are annealed out at 900 C. However, for the P
C. However, for the P -implanted sample, it was shown that a much weaker agglomeration process of the vacancy clusters compared with Al
-implanted sample, it was shown that a much weaker agglomeration process of the vacancy clusters compared with Al implantation. A higher annealing temperature of 1100
implantation. A higher annealing temperature of 1100 C is needed to fully remove these vacancies.
C is needed to fully remove these vacancies.